Learn How to Choose RFID Readers/Writers in 5 Minutes
Learn How to Choose RFID Readers/Writers in 5 Minutes
The Importance of RFID Technology
RFID technology uses radio waves for object identification and data exchange, significantly improving recognition speed and accuracy. Unlike traditional barcode technology, RFID supports contactless operations, overcoming the limitation of scanners requiring direct contact with tags.
For a deeper understanding of RFID technology principles, its technical advantages, and application examples, check out this article: "How to Choose the Right RFID Module? Technical Advantages and Application Examples"
Four Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an RFID Reader/Writer
These four key factors will help you select the right RFID reader to enhance efficiency!
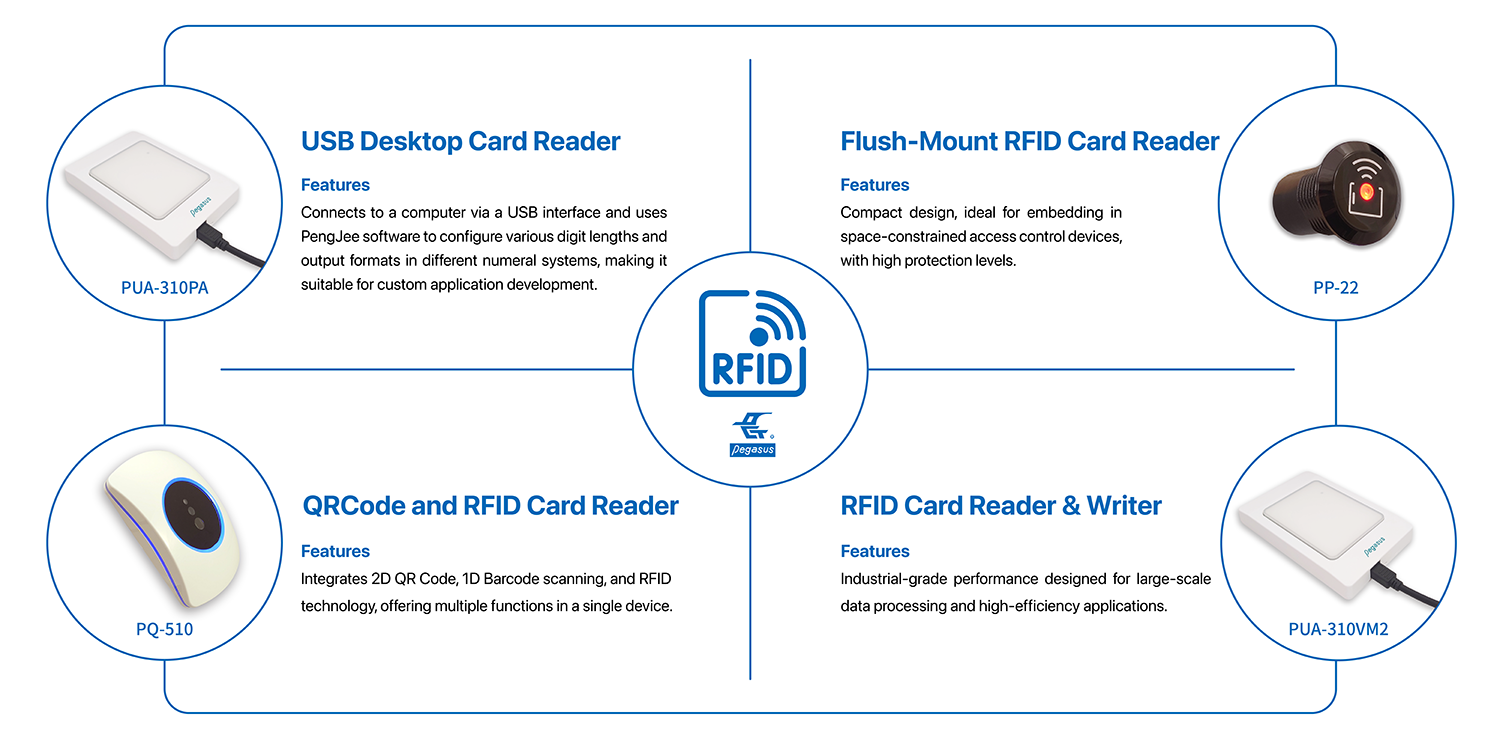
PONGEE’s Popular RFID Reader/Writer Specifications Comparison
PONGEE Recommendations: Tailored RFID Reader Solutions
1. For custom application development: Choose USB desktop RFID reader for convenient USB connectivity.
2. For multi-method identification systems: Opt for QR Code & RFID Reader to support both technologies simultaneously.
3. For space-constrained environments: Select Mini Embedded RFID Reader designed for compact applications.
4. For serial communication and personnel identity verification: Choose RFID Card Reader and Writer for reliable performance and versatile interface options.
Advantages of PONGEE Products
● Innovative Features: The PQ-510 combines QR code and RFID technologies for versatile applications.
● High Protection Standards: The PP-22 leads its category with an IP68 rating, suitable for harsh environments.
● User-Friendly Design: The PUA-310PA offers ease of use, while the PUA-310VM2 supports multiple interfaces for integration efficiency.
● Professional Support: PONGEE provides comprehensive technical support to ensure product stability and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
● What’s the difference between RFID and barcode technology?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and barcode technology differ primarily in identification methods and range.
○ Barcodes rely on visual recognition using scanners that must directly align with and contact the barcode, functioning over a short range.
○ RFID uses radio frequencies for data transfer, allowing contactless identification over longer distances and simultaneous reading of multiple tags, making it ideal for high-efficiency, long-range applications.
● What is the difference between MIFARE and ISO 14443?
MIFARE is an application of the ISO 14443 standard, primarily used for contactless smart cards like access control and transit cards. ISO 14443 is a general industry standard, while MIFARE offers a branded and specific implementation tailored for various applications.
● What does the IP rating mean?
An IP rating represents a device's resistance to dust and water. It typically consists of "IP" followed by two numbers.
○ The first number (0-6) indicates dust resistance, with higher numbers offering better protection.
○ The second number (0-9) indicates water resistance, with higher numbers providing stronger waterproof capabilities.
For example, an IP68 rating signifies complete dust protection and the ability to withstand extended submersion in water.
Choosing the right RFID reader is the foundation for improved efficiency. With a diverse product range, high-performance designs, and exceptional support, PONGEE offers smart solutions for various industries.
Contact us at Pongee to learn more about RFID technology and solutions, and let's work together to push your business toward a smarter, more efficient future!
RFID technology uses radio waves for object identification and data exchange, significantly improving recognition speed and accuracy. Unlike traditional barcode technology, RFID supports contactless operations, overcoming the limitation of scanners requiring direct contact with tags.
For a deeper understanding of RFID technology principles, its technical advantages, and application examples, check out this article: "How to Choose the Right RFID Module? Technical Advantages and Application Examples"
Four Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an RFID Reader/Writer

These four key factors will help you select the right RFID reader to enhance efficiency!

PONGEE’s Popular RFID Reader/Writer Specifications Comparison
| Product Name | Frequency | Interface | IP Rating | Application | Features |
| PUA-310PA | 13.56 MHz | USB | None | Ideal for custom application development | Plug-and-play USB-powered device. No external power needed. Flexible format settings for output. |
| PQ-510 | 125KHz / 13.56 MHz | UART / RS-232 / RS-485 / USB / TCP/IP / OSDP | IP54 | Access control, rental systems, attendance management | Supports QR code and RFID; QR code for one-time or valid-period usage, reducing card replacement costs. |
| PP-22 | 13.56 MHz | Wiegand/UART | IP68 | Compact personnel access control (e.g., lockers) | Waterproof and dustproof with IP68 rating. |
| PUA-310VM2 | 13.56 MHz | USB, RS-232, RS-485 | IP54 | Logistics, ID management, smart parking, and more | Supports RFID card reading and writing for versatile applications. |
PONGEE Recommendations: Tailored RFID Reader Solutions
1. For custom application development: Choose USB desktop RFID reader for convenient USB connectivity.
2. For multi-method identification systems: Opt for QR Code & RFID Reader to support both technologies simultaneously.
3. For space-constrained environments: Select Mini Embedded RFID Reader designed for compact applications.
4. For serial communication and personnel identity verification: Choose RFID Card Reader and Writer for reliable performance and versatile interface options.
Advantages of PONGEE Products
● Innovative Features: The PQ-510 combines QR code and RFID technologies for versatile applications.
● High Protection Standards: The PP-22 leads its category with an IP68 rating, suitable for harsh environments.
● User-Friendly Design: The PUA-310PA offers ease of use, while the PUA-310VM2 supports multiple interfaces for integration efficiency.
● Professional Support: PONGEE provides comprehensive technical support to ensure product stability and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
● What’s the difference between RFID and barcode technology?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and barcode technology differ primarily in identification methods and range.
○ Barcodes rely on visual recognition using scanners that must directly align with and contact the barcode, functioning over a short range.
○ RFID uses radio frequencies for data transfer, allowing contactless identification over longer distances and simultaneous reading of multiple tags, making it ideal for high-efficiency, long-range applications.
● What is the difference between MIFARE and ISO 14443?
MIFARE is an application of the ISO 14443 standard, primarily used for contactless smart cards like access control and transit cards. ISO 14443 is a general industry standard, while MIFARE offers a branded and specific implementation tailored for various applications.
● What does the IP rating mean?
An IP rating represents a device's resistance to dust and water. It typically consists of "IP" followed by two numbers.
○ The first number (0-6) indicates dust resistance, with higher numbers offering better protection.
○ The second number (0-9) indicates water resistance, with higher numbers providing stronger waterproof capabilities.
For example, an IP68 rating signifies complete dust protection and the ability to withstand extended submersion in water.
Choosing the right RFID reader is the foundation for improved efficiency. With a diverse product range, high-performance designs, and exceptional support, PONGEE offers smart solutions for various industries.
Contact us at Pongee to learn more about RFID technology and solutions, and let's work together to push your business toward a smarter, more efficient future!

 Compare
Compare
