How to Choose the Right RFID Module?
How to Choose the Right RFID Module? Technical Advantages and Application Examples
Basic Principles of RFID Modules
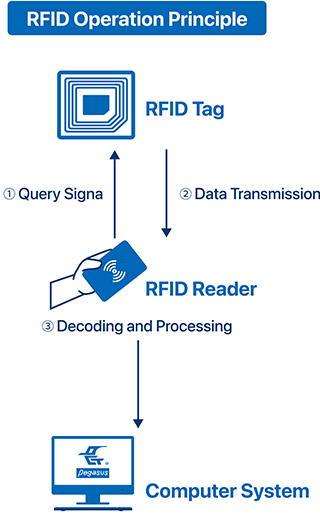
An RFID system consists of three main components: RFID tags, RFID readers, and backend computer systems. When an RFID tag enters the reader's signal range, the reader sends a signal to the tag, and the tag returns the stored data, which is then transmitted to the backend system for processing and decoding. Depending on the application requirements, the reader can also perform data writing operations to update information on the RFID tag.
Application Example:
For UHF RFID modules, in the logistics sector, RFID technology can accurately track the transportation process of goods, enable real-time monitoring, and improve inventory management efficiency.
RFID Application Scenarios
The wide application of RFID technology has promoted automation and digital upgrades across many industries. Here are several key application scenarios:
 Technical Advantages and Limitations of RFID Modules
Technical Advantages and Limitations of RFID Modules
Technical Limitations
How to Choose the Right RFID Module
Choosing the right RFID module is crucial for enhancing business automation. Consider the following factors:
Product Recommendations:
To help you select the right RFID module, we recommend the following high-performance products, each offering tailored solutions for different needs:
Fixed vs. Handheld RFID Readers
When selecting RFID readers, the choice between fixed and handheld readers will directly affect work efficiency and cost. Different application needs determine which type of reader is most suitable for your business.
Future Trends
RFID technology is evolving toward more efficient and intelligent solutions, particularly in the context of IoT and smart devices. In the future, RFID technology will further integrate into smart cities, smart transportation, public safety, and other fields, leading to more innovative applications. With the development of RFID technology, we expect to see more automated and intelligent RFID applications in the future.
Conclusion
Choosing the right RFID module is essential for achieving business automation and data management. By selecting the right module based on your needs, you can significantly increase operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and bring higher operational benefits to your business. Our RFID module series, with its high performance, stability, and diverse application scenarios, will help you stay ahead in your future business development.
Contact us at Pongee to learn more about RFID technology and solutions, and let's work together to push your business toward a smarter, more efficient future!
An RFID system consists of three main components: RFID tags, RFID readers, and backend computer systems. When an RFID tag enters the reader's signal range, the reader sends a signal to the tag, and the tag returns the stored data, which is then transmitted to the backend system for processing and decoding. Depending on the application requirements, the reader can also perform data writing operations to update information on the RFID tag.

RFID systems operate at different frequencies, which can be categorized as follows:
- Low Frequency (LF): Suitable for short-range identification, commonly used in animal tracking.
- High Frequency (HF): Commonly used for access control systems, transit cards, and other short-range applications.
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF): Ideal for long-range identification, widely used in logistics and warehouse management.
Application Example:
For UHF RFID modules, in the logistics sector, RFID technology can accurately track the transportation process of goods, enable real-time monitoring, and improve inventory management efficiency.
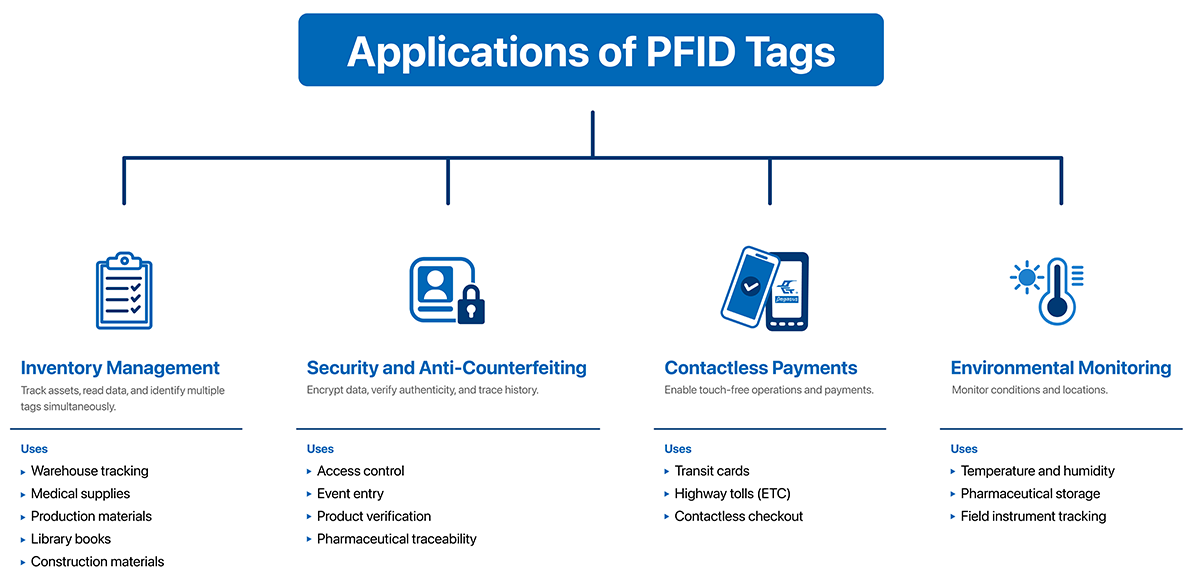
RFID Application Scenarios
The wide application of RFID technology has promoted automation and digital upgrades across many industries. Here are several key application scenarios:
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management:
RFID technology efficiently tracks the transportation process of goods, enabling end-to-end monitoring from raw materials to finished products, enhancing inventory management. RFID tags can be easily embedded in product packaging for seamless tracking and real-time updates.
- Access Control and Attendance Management:
RFID-based access control systems are contactless, providing more convenient and efficient entry and exit control. Similarly, RFID attendance systems can accurately record employee clock-in and clock-out times, eliminating manual entry errors and saving time.
- Asset Management:
RFID technology can be used to label and track equipment and assets in environments such as schools, hospitals, and enterprises, enabling automated asset management and reducing asset loss and management costs.
- Retail and Theft Prevention:
RFID technology can help retailers efficiently manage inventory and prevent theft. RFID tags embedded in products can trigger alarms when the items pass through anti-theft gates.

Technical Advantages
| Advantages | Explanation |
| Long-Range Identification | Depending on the RFID frequency, some modules can identify tags within a range of several meters, particularly suitable for applications requiring long-range identification, such as logistics management. |
| Simultaneous Multi-Tag Identification | Modules can identify multiple tags simultaneously, improving efficiency, especially in scenarios where large volumes of tags need to be processed at once, such as in warehouse management. |
| Contactless Reading | Tags can be identified without physical contact, avoiding mechanical wear, and ensuring longer durability of the tags. |
| Strong Adaptability | RFID modules operate stably in various environments (e.g., indoors, outdoors, or harsh industrial environments) and are less affected by environmental factors. |
Technical Limitations
| Limitations | Explanation |
| Higher Costs | The initial investment in RFID systems is higher than barcode systems, especially in terms of tag and reader prices. However, it offers greater security compared to barcode systems. |
| Signal Interference | Metals and liquids can interfere with RFID signals, making identification less accurate or reducing the effective range in certain environments. |
| Range Limitations | Although UHF modules provide long-range identification, their range may be significantly reduced in environments with metals or water. |
How to Choose the Right RFID Module
Choosing the right RFID module is crucial for enhancing business automation. Consider the following factors:
- Frequency Requirements:
- Read Range:
- System Compatibility:
- Installation Environment:
- Cost Budget:
Product Recommendations:
To help you select the right RFID module, we recommend the following high-performance products, each offering tailored solutions for different needs:
| Model | Frequency | Feature Description | Applicable Scenarios |
| PIDF-20W26 | 125KHz & 13.56MHz | Dual-frequency reading module, supports various card protocols | For applications requiring multi-frequency capabilities |
| PIEH-FWAS-14H22 | 125KHz EM & H.I.D. | Dual decoding module, suitable for multiple applications | Access control, attendance, asset management, etc. |
| PIMF-18EU1 | 13.56MHz Mifare | Efficient identification, stable operation | Asset management, campus management |
| PIMF-02BK | 13.56MHz Mifare read & write | Supports multiple protocols, anti-collision, ideal for high-efficiency multi-card operations | Warehouse, logistics, data reading scenarios |
Fixed vs. Handheld RFID Readers
When selecting RFID readers, the choice between fixed and handheld readers will directly affect work efficiency and cost. Different application needs determine which type of reader is most suitable for your business.
| Type | Fixed RFID Reader | Handheld RFID Reader |
| Application Scenarios | Suitable for long-term, stable reading in fixed locations like warehouses, entry/exit points, and conveyor belts | Suitable for mobile scenarios such as inventory checks, equipment inspections, and temporary data reading |
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
Future Trends
RFID technology is evolving toward more efficient and intelligent solutions, particularly in the context of IoT and smart devices. In the future, RFID technology will further integrate into smart cities, smart transportation, public safety, and other fields, leading to more innovative applications. With the development of RFID technology, we expect to see more automated and intelligent RFID applications in the future.
Conclusion
Choosing the right RFID module is essential for achieving business automation and data management. By selecting the right module based on your needs, you can significantly increase operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and bring higher operational benefits to your business. Our RFID module series, with its high performance, stability, and diverse application scenarios, will help you stay ahead in your future business development.
Contact us at Pongee to learn more about RFID technology and solutions, and let's work together to push your business toward a smarter, more efficient future!

 Compare
Compare
